Why is protein important for the body?
Protein can be found all throughout the body, including muscle, bone, skin, hair, and nearly every other bodily component. It is the building block of the enzymes facilitating numerous chemical reactions and the hemoglobin responsible for transporting oxygen in the bloodstream. Protein is also essential for the growth, maintenance, and repair of tissues in our bodies. With over 10,000 different proteins shaping and sustaining our physiological makeup, protein serves as a cornerstone of our existence.
Proteins are made up of smaller parts called amino acids. Our bodies can't store these amino acids, so we either make them from scratch or modify others to get what we need. There are nine special amino acids, called essential amino acids, that we have to get from the food we eat. When we consume protein, it breaks down into amino acids, which are then used to repair cells, support immune function, and produce enzymes and hormones crucial for various bodily processes.
How much protein do you need?
The suggested daily intake of protein for a healthy adult engaging in minimal physical activity stands at 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight (BW). For individuals with varying levels of physical activity, the recommended protein intake increases to 1.0, 1.3, and 1.6 grams per kilogram of BW per day for those with minimal, moderate, and intense physical activity, respectively. It's deemed safe for healthy adults to consume protein long-term at a rate of 2 grams per kilogram of BW per day, with a maximum tolerable upper limit of 3.5 grams per kilogram of BW per day for well-adapted individuals. However, sustained high protein intake, exceeding 2 grams per kilogram of BW per day in adults, may lead to gastrointestinal, renal, and vascular issues and is advised against. Both the quantity and quality of protein play pivotal roles in its nutritional benefits. Therefore, ensuring adequate intake of high-quality proteins from animal sources such as lean meat and dairy products is crucial for optimal human growth, development, and overall health.
What foods have protein?
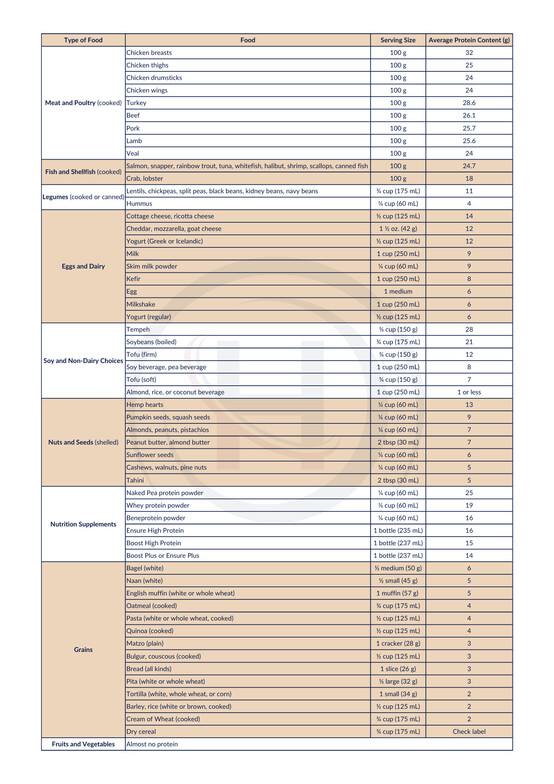
Protein-rich foods encompass a variety of options such as meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes (including dried beans, peas, and lentils), soy products, nuts, and seeds. While grain products contain some protein, fruits and vegetables have almost no protein. The following chart is a list of common foods and the average amount of protein content per serving size for each food item. This information was gathered from Sunnybrook Odette Cancer Centre.
See below to download a summary chart of common protein sources in everyday foods.

HealthyToDos Inc.
Contact Me


